Redis Explained
Source
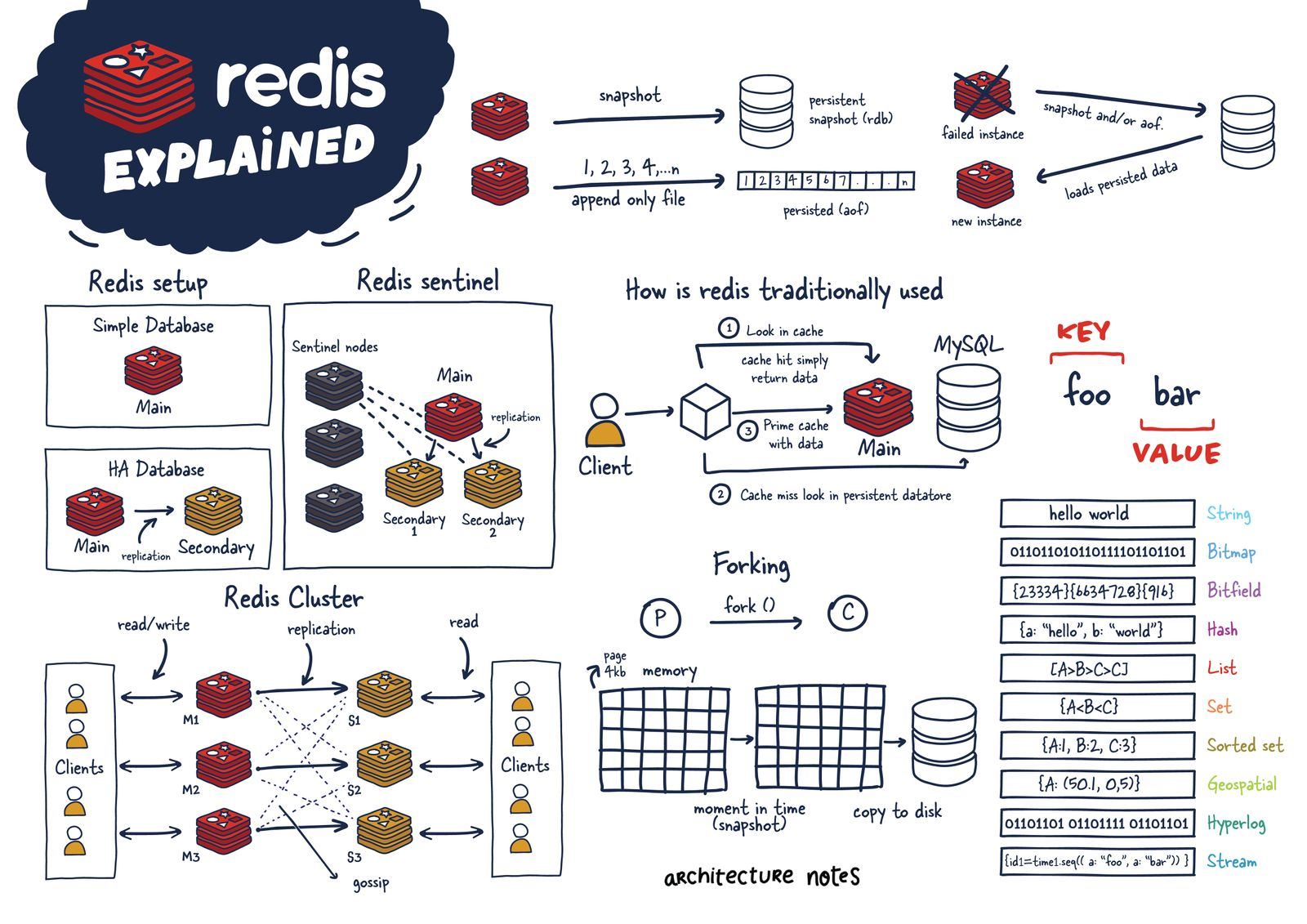
- Redis (REmote DIctionary Service) - key-value db
- In-memory database, backup to disk
- Use as cache in the past
- Like Memcached, but more features
- Many architecture configurations supported
- Single instance - Main db only
- HA (High Availability) - Has replications to secondary db
- Sentinel - Has Sentinel(s) to monitor main & secondaries
- Cluster - Horizontal scaling, gossipping nodes
- Many persistence models
- No persistence
- RDB (Redis Database) file - Save db as file snapshot, faster than AOF
- AOF (Append Only File) - Log write operations to be replayed again, more durable that RDB
- Flushes to disk with fsync when possible
- RDB + AOF - More durable but slower
- Forking - OS creates process copy, but shares memory with copy-on-write technique
- Redis uses this technique to persist the data performantly.
